Nvidia Profile Inspector
 |
|
| Developers | |
|---|---|
| Orbmu2k | |
| Release dates | |
| Windows | June 20, 2010[1] |
Nvidia Profile Inspector (NPI) is an open source third-party tool created for pulling up and editing application profiles within the Nvidia display drivers. It works much like the Manage 3D settings page in the Nvidia Control Panel but goes more in-depth and exposes settings and offers functionality not available through the native control panel.
The tool was spun out of the original Nvidia Inspector which featured an overclocking utility and required the user to create a shortcut to launch the profile editor separately.
Nvidia Profile Inspector typically sees maintenance updates released every couple of months, keeping it aligned with changes introduced in newer versions of the drivers, although the project were seemingly on a hiatus between January 19, 2021 and November 13, 2022. An unofficial fork was released in April 2022 with improved support for newer drivers and now no longer available since an official update from the original author.
General information
- HBAO+ Compatibility Flags
- Anti-Aliasing Compatibility Flags
- SLI Compatibility Flags (German)
- Official repository
Related articles
Availability
| Source | DRM | Notes | Keys | OS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Official website |
Installation
| Instructions |
|---|
Status indicators
|
First steps for tweaking driver settings
| Select (or create if missing) the display driver profile for the game |
|---|
|
Video
Anisotropic filtering (AF)
- This is an example of why it may be relevant to force high texture filtering globally as some developers' own solutions might not be as high quality as they could be.
- There is a risk of negative side effects occurring in some games as a result of a forced global driver-level override, with unexpected consequences ranging from textures looking wrong to some post-processing shaders being affected if they rely of a texture that have an unintended level of filtering applied to it. If Nvidia becomes aware of a game that has a conflict with driver forced texture filtering, they may set a special flag on the game profile for texture filtering that disables driver overrides for that game, such as with Far Cry 3 and Doom (2016), though this is not a guarantee as proper in-depth compatibility testing is impossible to perform for all games.[2]
- A quicker way of doing this is to use Nvidia Control Panel and set Anisotropic filtering to
16xand Texture filtering - Quality toHigh qualityunder Manage 3D settings > Global Settings.
| Force highest available texture filtering settings system-wide |
|---|
|
Ambient occlusion (AO)
| Force HBAO+ for a select game |
|---|
|
Layer Vulkan/OpenGL on DXGI swapchain
- Layering Vulkan and OpenGL games on a DXGI swapchain allows for improved multitasking and using Auto HDR on Windows 11.[3]
| Instructions:[4] |
|---|
|
Misc tweaks
Prevent Ansel from being injected/enabled for a specific game
- Using Nvidia Profile Inspector, is becomes possible to disable Ansel on a per-game basis if desired.
- The display drivers loads Ansel related DLL files into all running applications they interface with by default, even if the application does not support or can make use of Ansel. This can cause issues for third-party tools or applications.
| Disable Ansel in the display driver profile for a specific game |
|---|
|
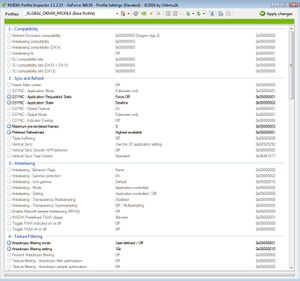
Settings
- Keep changes to the base
_GLOBAL_DRIVER_PROFILEprofile limited, as overrides there are applied to all games and applications.
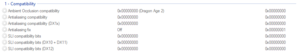
Compatibility
- Compatibility parameters that allows ambient occlusion, anti-aliasing, and SLI to be used for games, if given an appropriate value.
- HBAO+ Compatibility Flags
- Anti-Aliasing Compatibility Flags
- SLI Compatibility Flags (German)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Ambient Occlusion compatibility | Allows HBAO+ to work with any given game. |
| Antialiasing compatibility | Allows various forms of anti-aliasing to work with any given DirectX 9 game. |
| Antialiasing compatibility (DX1x) | Allows various forms of anti-aliasing to work with DirectX 10/11/12 games. Often restricted to MSAA and generally sees little use due to its limited capability. |
| Antialiasing Fix | Avoid black edges in some games while using MSAA.[5] Related to Team Fortress 2 and a few other games as well, where it is enabled by default. |
| SLI compatibility bits | Allows SLI to work in any given DirectX 9 game. |
| SLI compatibility bits (DX10+DX11) | Allows SLI to work in any given DirectX 10/11 game. |
| SLI compatibility bits (DX12) | Allows SLI to work in any given DirectX 12 game. |
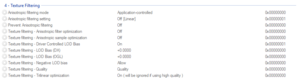
Sync and Refresh
- See Frame rate (FPS) for relevant information.
- The built-in frame rate limiter of the Nvidia display drivers introduces 2+ frames of delay, while RTSS (and possibly other alternatives) only introduces 1 frame of delay.[6]
- AnandTech - Triple Buffering: Why We Love It - Recommended reading about triple buffering/Fast Sync.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Flip Indicator | Enables an on-screen display of frames presented using flip model. |
| Frame Rate Limiter | Enables the built-in frame rate limiter of the display drivers at the specified FPS. |
| Frame Rate Limiter Mode | Controls what mode of the frame rate limiter will be used. |
| GSYNC - Application Mode | Controls whether the G-Sync feature will be active in fullscreen only, or in windowed mode as well. |
| GSYNC - Application Requested State | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
| GSYNC - Application State | Selects the technique used to control the refresh policy of an attached monitor.
It is highly recommended to change this using the Nvidia Control Panel > Manage 3D Settings > Monitor Technology instead to properly configured this and related parameters. |
| GSYNC - Global Feature | Toggles the global G-Sync functionality. It is recommended to change this using the Nvidia Control Panel > Set up G-SYNC instead to properly configured this and related parameters. |
| GSYNC - Global Mode | Controls whether the G-Sync feature will be active globally in fullscreen only, or in windowed mode as well. |
| GSYNC - Indicator Overlay | Enables a semi-transparent on-screen status indicator of when G-Sync is being used. If G-Sync is not being used, the indicator is not shown at all. |
| GSYNC - Support Indicator Overlay | Enables a diagnostics overlay which updates in real time. Can help determine which type of G-SYNC is being requested by a particular 3d application (is it requesting Exclusive Fullscreen or Windowed mode?) |
| Maximum pre-rendered frames | Controls how many frames the CPU can prepare ahead of the frame currently being drawn by the GPU. Increasing this can result in smoother gameplay at lower frame rates, at the cost of additional input delay.[7] This setting does not apply to SLI configurations.
|
| Preferred Refresh Rate | Controls the refresh rate override of the display drivers for games running in exclusive fullscreen mode. This also dictates the upper limit of the G-Sync range, as G-Sync will go inactive and the screen will start to tear at frame rates above the configured refresh rate, or V-Sync will kick in and sync the frame rate to the refresh rate if enabled.
|
| Triple buffering | Toggles triple buffering in OpenGL games. Enabling this improves performance when vertical sync is also turned on. |
| Vertical Sync | Controls vertical sync, or enables Fast Sync. Fast-Sync is essentially triple buffering for DirectX games, and is only applicable to frame rates above the refresh rate when regular V-Sync is disabled. |
| Vertical Sync Smooth AFR behavior | Toggles V-Sync smoothing behavior when V-Sync is enabled and SLI is active.
Official description:[9] Smooth Vsync is a new technology that can reduce stutter when Vsync is enabled and SLI is active. When SLI is active and natural frame rates of games are below the refresh rate of your monitor, traditional Vsync forces frame rates to quickly oscillate between the refresh rate and half the refresh rate (for example, between 60 Hz and 30 Hz). This variation is often perceived as stutter. Smooth Vsync improves this by locking into the sustainable frame rate of your game and only increasing the frame rate if the game performance moves sustainably above the refresh rate of your monitor. This does lower the average framerate of your game, but the experience in many cases is far better. |
| Vertical Sync Tear Control | Toggles Adaptive V-Sync when vertical sync is enabled. Not available when G-Sync is enabled.
Official description:[10] Nothing is more distracting than frame rate stuttering and screen tearing. The first tends to occur when frame rates are low, the second when frame rates are high. Adaptive VSync is a smarter way to render frames using Nvidia Control Panel software. At high framerates, VSync is enabled to eliminate tearing. At low frame rates, it's disabled to minimize stuttering. |
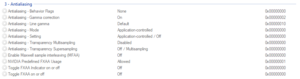
Antialiasing
- See Anti-aliasing (AA) for relevant information.
- Anti-Aliasing Compatibility Flags
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Antialiasing - Behavior Flags | These mostly exist as a method of governing usage of AA from Nvidia Control Panel, though they also affect Inspector as well.
|
| Antialiasing - Gamma Correction | Gamma correction for MSAA.
|
| Antialiasing - Line gamma | Applies gamma correction for singular lines (like wires) as compared to edges.[12] |
| Antialiasing - Mode | Determines in what mode the anti-aliasing override of the display driver should function in for an application:
|
| Antialiasing - Setting |
This is where the specific method of forced/enhanced MSAA or OGSSAA is set. |
| Antialiasing - Transparency Multisampling |
|
| Antialiasing - Transparency Supersampling |
|
| Enable Maxwell sample interleaving (MFAA) |
This enables Nvidia's Multi Frame Anti Aliasing mode. This only works in DXGI (DX10+) and requires either the game to have MSAA enabled in the game or MSAA to be forced.
What it does is change the sub sample grid pattern every frame and then is reconstructed in motion with a "Temporal Synthesis Filter" as Nvidia calls it.
|
| Nvidia Predefined FXAA Usage | Controls whether Nvidia's FXAA implementation is allowed to be enabled for an application through Nvidia Control Panel (primarily) or Nvidia Profile Inspector. |
| Toggle FXAA indicator on or off | This will display a small green icon in the left upper corner if enabled showing whether FXAA is enabled or not. |
| Toggle FXAA on or off | FXAA is a fast shader-based post-processing technique that can be applied to any application, including those which do not support other forms of hardware-based antialiasing. FXAA can also be used in conjunction with other antialiasing settings to improve overall image quality.
|
Enhance application setting
- When overriding the in-game MSAA fails, you can instead replace (enhance) the in-game MSAA with the Nvidia MSAA technique of your choice.
- These usually require anti-aliasing compatibility flags to work properly in DirectX 9 applications; see the List of anti-aliasing compatibility flags.
- The level of supersampling must match a corresponding level of MSAA. For example, if 4x MSAA is used, then 4x Sparse Grid Supersampling must be used.
- In OpenGL
Supersamplingis equivalent toSparse Grid Supersampling. Ergo, 4xMSAA+4xTrSSAA will give you 4xFSSGSSAA in OpenGL games that work.
Supersampling
- Inexpensive
- Does not require MSAA to work
- Only works on alpha-tested surfaces
Full-Screen Sparse Grid Supersamping
- Extremely high-quality supersampling
- Works on the entire image
- Requires MSAA to work
- Very expensive
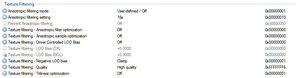
Texture Filtering
- See Anisotropic filtering (AF) for relevant information.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Anisotropic filtering mode | Toggles the built-in anisotropic filtering override of the display drivers.
|
| Anisotropic filtering setting | Controls the level of texture filtering the driver override applies, if Anisotropic filtering mode is set to User-defined / Off.
|
| Prevent anisotropic filtering | Similar to AA Behavior Flags, if this is set to On it will ignore user-defined driver overrides. Some games default to this, such as Quake 4, RAGE, Doom (2016), Far Cry 3, and Far Cry 3: Blood Dragon.
|
| Texture filtering - Anisotropic filter optimization | Anisotropic filter optimization improves performance by limiting trilinear filtering to the primary texture stage where the general appearance and color of objects is determined. Bilinear filtering is used for all other stages, such as those used for lighting, shadows, and other effects. This setting only affects DirectX programs.
|
| Texture Filtering - Anisotropic sample optimization | Anisotropic sample optimization limits the number of anisotropic samples used based on texel size. This setting only affects DirectX programs.
|
| Texture Filtering - Driver Controlled LOD Bias | When using SGSSAA with this enabled will allow the driver to compute its own negative LOD bias for textures to help improve sharpness (at cost of potential for more aliasing) for those who prefer it. It's generally less than the fixed amounts that are recommended.[citation needed]
|
| Texture Filtering - LOD Bias (DX) |
The level of detail bias setting for textures in DirectX applications. This normally only works under 2 circumstances, both of which requires Driver Controlled LoD Bias set to
Notes:
|
| Texture Filtering - LOD Bias (OGL) | Identical to Texture Filtering - LOD Bias (DX) but applies to OpenGL applications instead. |
| Texture Filtering - Negative LOD bias | Some applications use negative LOD bias to sharpen texture filtering. This sharpens the stationary image but introduces aliasing ("shimmering") when the scene is in motion. This setting controls whether negative LOD bias are clamped (not allowed) or allowed. |
| Texture Filtering - Quality | This setting allows you to decide if you would prefer performance, quality, or a balance between the two. If you change this using the Nvidia Control Panel, the control panel will make all of the appropriate texture filtering adjustments based on the selected preference.
|
| Texture Filtering - Trilinear Optimization | Trilinear optimization improves texture filtering performance by allowing bilinear filtering on textures in parts of the scene where trilinear filtering is not necessary. This setting only affects DirectX applications.
|
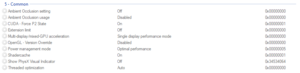
Common
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Ambient Occlusion setting | This setting determines what mode of ambient occlusion is to be used when forced in games with no built-in support for it:
|
| Ambient Occlusion usage | Set this to Enabled when using forced ambient occlusion.
|
| CUDA - Force P2 State | If set to OFF it forces GPU into P0 State for compute. |
| Extension limit | Extension limit indicates whether the driver extension string has been trimmed for compatibility with particular applications. Some older applications cannot process long extension strings and will crash if extensions are unlimited.
|
| Multi-display/mixed-GPU acceleration | This controls GPU-based acceleration in OpenGL applications and will have no effect on performance on DirectX platforms.[18] |
| OpenGL - Version Override | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
| Optimize for Compute Performance | This setting is intended to provide additional performance to non-gaming applications that use large CUDA address spaces and large amounts of GPU memory when run on graphics cards based on second-generation Maxwell GPUs. Graphics cards based on other architectures do not utilize this setting.[19] |
| Power management mode | This allows you to set a preference for the performance level of the graphics card when running 3D applications. It is recommended to configure this on a per-game basis using game-specific profiles, to prevent unnecessary power draw while not gaming.
|
| Shader cache | Enables or disables the shader cache, which saves compiled shaders to your hard drive to improve game performance.[21]
|
| Show PhysX Visual Indicator | Enables an on-screen status indicator of when PhysX is being used. If PhysX is not being used, the indicator is not shown at all. |
| Threaded optimization | Allows OpenGL applications to take advantage of multiple CPUs.
|
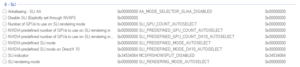
SLI
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Antialiasing - SLI AA | This determines whether a Nvidia SLI setup splits the MSAA workload between the available GPUs.[22] |
| Disable SLI (Explicitly set through NVAPI) | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
| Number of GPUs to use on SLI rendering mode | Forces all rendering modes to utilize either one, two, three or four gpu's for rendering. |
| NVIDIA predefined number of GPUs to use on SLI rendering mode | Forces DX9 and OpenGl to utilize either one, two, three or four gpu's for rendering. |
| NVIDIA predefined number of GPUs to use on SLI rendering mode on DX10 | Forces DX10, DX11 and DX12 to utilize either one, two, three or four gpu's for rendering. This can effect total bandwidth not using four but using four rather than 2 can cause artifacting in certain games. |
| NVIDIA predefined SLI mode | Forces DX9 and OpenGl to render using AFR, AFR 2, SFR (CFR) or Single Gpu Mode with Sli Enabled in Nvidia Control Panel. |
| NVIDIA predefined SLI mode on DX10 | Forces DX10, DX11 and DX12 to render using AFR, AFR 2, SFR (CFR) or Single Gpu Mode with Sli Enabled in Nvidia Control Panel. Almost all games require AFR in DX11. Nvlink with turing allows for CFR to be used in several games where AFR is not even usable. |
| SLI indicator | Enables a semi-transparent on-screen status indicator of when SLI is being used and how the workload is split between the cards. |
| SLI rendering mode | Forces Base sli rendering mode AFR, AFR 2, SFR (CFR) or Single Gpu Mode with Sli Enabled in Nvidia Control Panel (Good for quick switching to test fps). Using this setting will override compatibility settings set in the sli section, this is why I call it Base Sli. |
Stereo
- Lists stereoscopic 3D settings related to Nvidia 3D Vision. More info can be found on Bo3b's School for Shaderhackers.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Force Stereo shuttering | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
| LaserXAdjust | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
| LaserYAdjust | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
| Stereo - Display mode | This setting allows you to choose the appropriate display mode for shutter glasses, stereo displays, and other hardware. Refer to the hardware documentation to determine which mode to use. |
| Stereo - Dongle Support | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
| Stereo - Enable | Enables stereo in OpenGL applications. |
| Stereo - Swap eyes | Select this option to exchange the left and right images. |
| Stereo - Swap mode | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
| StereoConvergence | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
| StereoCutoff | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
| StereoCutoffDepthFar | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
| StereoCutoffDepthNear | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
| StereoFlagsDX10 | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
| StereoMemoEnabled | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
| StereoProfile | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
| StereoTextureEnable | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
| StereoUseMatrix | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
Other
- Lists settings which do not match another category.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Ansel flags for enabled applications | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
| Application Profile Notification Popup Timeout | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
| Battery Boost | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
| Buffer-flipping mode | Determines how the video buffer is copied to the screen. This setting only affects OpenGL and Vulkan programs.
|
| Deep color for 3D applications | Toggles 30-bit (10 bpc) deep color on compatible monitors on Quadro cards. Affects only OpenGL (windowed and fullscreen) and Direct3D 10 (fullscreen mode only). See this technical brief for further information. |
| Display the VRR Overlay Indicator | Draws a G-Sync logo when an application engages G-Sync. |
| Do not display this profile in the Control Panel | Hides the profile from being listed in Nvidia Control Panel > Manage 3D Settings > Program Settings. |
| Enable Ansel | Toggles Ansel (NvCamera) for the application. This is enabled by default and results in the display drivers injecting the DLL files for Ansel in all applications. |
| Enable application for Optimus | On an Optimus laptop, controls whether the selected application runs on the dedicated Nvidia GPU or the integrated GPU. |
| Enable GTX950 specific features | Enables GTX 950 latency optimizations on E-Sports Titles (Dota 2, Heroes of the Storm, League of Legends) |
| Enable NV_gpu_multicast extension | This extension enables novel multi-GPU rendering techniques by providing application control over a group of linked GPUs with identical hardware configuration. This setting only affects OpenGL programs. |
| Enable overlay | Allows the use of OpenGL overlay planes in programs. Typically used if a program fails to render OpenGL planes. |
| Event Log Severity Threshold | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. This setting only affects OpenGL programs. |
| Event Log Tmon Severity Threshold | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. This setting only affects OpenGL programs. |
| Export Performance Counters | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
| Export Performance Counters for DX9 only | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
| Exported Overlay pixel types | Determines whether the driver supports RGB or color indexed OpenGL overlay plane formats. Typically used if a program fails to set the proper OpenGL overlay plane format. |
| Frame Rate Monitor | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
| Frame Rate Monitor Control | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
| High level control of the rendering quality on OpenGL | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
| ICafe Settings | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
| List of Universal GPU ids | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
| Maximum AA samples allowed for a given application | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
| Maximum frames allowed | Redundant setting for "Maximum pre-rendered frames". If set from the Nvidia Control Panel, both this and "Maximum pre-rendered frames" will be updated. |
| Maximum GPU Power | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. (Not available in version 1.9.7.3) |
| Maximum resolution alllowed for a given application | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
| Memory Allocation Policy | This defines how workstation feature resource allocation is performed.
|
| NVIDIA Predefined Ansel Usage | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
| NVIDIA Quality upscaling | Uses a lanczos upscaling filter instead of a bilinear one. The result is a less blurry fullscreen picture at less than native resolutions. |
| OpenGL default swap interval | Toggles Vertical Sync behaviour, but specifically for OpenGL applications.
|
| OpenGL default swap interval fraction | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
| OpenGL default swap interval sign | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
| Optimus flags for enabled applications | Select which GPU is used when launching the application.
|
| PowerThrottle | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
| Preferred OpenGL GPU | Select the GPU to be used by OpenGL applications. |
| Quiet Mode | Quiet Mode/Whisper Mode, Select ON/OFF [Makes Laptop/GPU Run Quieter] |
| Quiet Mode Application FPS | When Quiet Mode Is Enabled, Set MAX FPS For Applications Using GPU in Quiet Mode |
| Shim Rendering Mode Options per application for Optimus | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
| SILK Smoothness | Silk reduces stutters in games caused by variable CPU or GPU workloads by smoothing out animation and presentation cadence using animation prediction and post render smoothing buffer.
|
| Steam Application ID | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
| Unified back/depth buffer | This setting is allows the OpenGL driver to allocate one back buffer and one depth buffer at the same resolution of the display. When this setting is enabled, OpenGL applications that create multiple windows use video memory more efficiently and show improved performance. When this setting is off, the OpenGL driver allocates a back buffer and depth buffer for every window created by an OpenGL application[23] |
| VAB Default Data | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
| Variable refresh Rate | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
| Virtual Reality pre-rendered frames | Limits the number of frames the CPU can prepare before the frames are processed by the GPU. Lower latency is preferable for virtual reality head sets. |
| Vsync - Behavior Flags | If you know what this setting does, please add a description here. |
Unknown
- These are unknown settings or overrides that Nvidia Profile Inspector is not aware of what they determine or controls.
- Most of these are game-specific overrides only applicable to a few games, or new flags that were introduced in newer versions of the display drivers.
- Not all unknown settings can be properly exported and imported at will. If a built-in profile using one of those have been removed, the recommendation is to reinstall the display drivers to ensure they are restored fully.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| 0x00666634 | When set to 1 (0x00000001), marks applications covered by the profile as a Silk Test App. This is required for the "SILK Smoothness" setting to take effect. |
| Parameter | Description |
| 0x10834FEE | When the parameter is set to 2 (0x0020000) the value modifies the speed of everything including the framerate that windows handles therefore it is better disabled because it renders ineffective the value of Nvidia framerate limiter v3 please refrain from modifying this value and leave it at the value 0x00000000 so that all applications work naturally |
References
- ↑ Verified by User:Aemony on 2020-07-24
- The original website dates v1.90 as having been released on June 20, 2010. This seems to have been the version that brought along with it the ability to tweak game/driver profile settings. The main Nvidia Profile tool itself was publicly released on April 24, 2010.
- ↑ Verified by User:Aemony on 2023-09-30
- An anisotropic filtering (AF) driver override is too widespread and have both subtle and obvious consequences that it is impossible to say for sure how "safe" it is to enforce. Many users are also not aware of its potential impact on textures and non-texture alike to the degree that a user can mistake a visual bug caused by an AF override as being either intentional or incompetency by the developers, or a minor visual glitch that the developers have not come around to fixing yet, and so users often end up dismissing the visual glitches, never realizing it is of their own creation.
- ↑ Reddit - /r/nvidia - PSA - You can now elevate OpenGL/Vulkan games to a DXGI Swapchain on today's drivers (526.47) - last accessed on 2023-01-16
- ↑ Verified by User:Aemony on 2023-01-16
- ↑ Geeks3D Forums - Nvidia Inspector 1.9.7.2 Beta - last accessed on 2018-08-29
- "added FERMI_SETREDUCECOLORTHRESHOLDSENABLE as "Antialiasing fix" to avoid black edges in some games while using MSAA (R320.14+)"
- ↑ Blur Busters - G-SYNC 101: In-game vs. External FPS Limiters - last accessed on
- "Needless to say, even if an in-game framerate limiter isn’t available, RTSS only introduces up to 1 frame of delay, which is still preferable to the 2+ frame delay added by Nvidia’s limiter with G-SYNC enabled, and a far superior alternative to the 2-6 frame delay added by uncapped G-SYNC."
- ↑ Maximum Pre-Rendered frames for SLI - last accessed on 2016-10-12
- "The 'maximum pre-rendered frames' function operates within the DirectX API and serves to explicitly define the maximum number of frames the CPU can process ahead of the frame currently being drawn by the graphics subsystem. This is a dynamic, time-dependent queue that reacts to performance: at low frame rates, a higher value can produce more consistent gameplay, whereas a low value is less likely to introduce input latencies incurred by the extended storage time (of higher values) within the cache/memory. Its influence on performance is usually barely measurable, but its primary intent is to control peripheral latency."
- ↑ DisplayLag - Reduce Input Lag in PC Games: The Definitive Guide - last accessed on 2018-08-29
- ↑ Nvidia - What is Smooth Vsync? - last accessed on 2018-08-29
- ↑ Nvidia - Adaptive VSync - last accessed on 2018-08-29
- ↑ NVIDIA's GeForce 8800 (G80): GPUs Re-architected for DirectX 10 - What's Gamma Correct AA? - last accessed on 2016-10-12
- ↑ GeForce Forums - What does "Line Gamma" do for Anti-Aliasing? - last accessed on 2018-08-30
- ↑ Verified by User:SirYodaJedi on 2019-09-10
- ↑ Verified by User:Aemony on 2018-08-30
- This is a comment by the modder Kaldaien in his Special K mod for Ys 8, which among other things included an anisotropic filtering override. The comment is shown while hovering the mouse over the anisotropic filtering override.
- ↑ Natural Violence - SGSSAA (archived 16 July 2018) - last accessed on 2016-10-12
- ↑ Negative LOD bias - Post #22 - last accessed on 9 June 2023
- ↑ Clamp negative LOD bias - last accessed on May 2023
- ↑ GeForce Forums - Mulit Display/Mixed GPU Acceleration How to use? - last accessed on 2018-08-30
- ↑ What does the setting "Optimize for Compute Performance" do? - last accessed on 2017-01-25
- ↑ https://nvidia.custhelp.com/app/answers/detail/a_id/3130/~/setting-power-management-mode-from-adaptive-to-maximum-performance
- ↑ GeForce 337.88 WHQL, Game Ready Watch Dogs Drivers Increase Frame Rates By Up To 75% - last accessed on 2016-10-12
- "Shaders are used in almost every game, adding numerous visual effects that can greatly improve image quality (you can see the dramatic impact of shader technology in Watch Dogs here). Generally, shaders are compiled during loading screens, or during gameplay in seamless world titles, such as Assassin's Creed IV, Batman: Arkham Origins, and the aforementioned Watch Dogs. During loads their compilation increases the time it takes to start playing, and during gameplay increases CPU usage, lowering frame rates. When the shader is no longer required, or the game is closed, it is discarded, forcing its recompilation the next time you play.
In today's 337.88 WHQL drivers we've introduced a new NVIDIA Control Panel feature called "Shader Cache", which saves compiled shaders to a cache on your hard drive. Following the compilation and saving of the shader, the shader can simply be recalled from the hard disk the next time it is required, potentially reducing load times and CPU usage to optimize and improve your experience.
By default the Shader Cache is enabled for all games, and saves up to 256MB of compiled shaders in %USERPROFILE%\AppData\Local\Temp\NVIDIA Corporation\NV_Cache. This location can be changed by moving your entire Temp folder using Windows Control Panel > System > System Properties > Advanced > Environmental Variables > Temp, or by using a Junction Point to relocate the NV_Cache folder. To change the use state of Shader Cache on a per-game basis simply locate the option in the NVIDIA Control Panel, as shown below."
- "Shaders are used in almost every game, adding numerous visual effects that can greatly improve image quality (you can see the dramatic impact of shader technology in Watch Dogs here). Generally, shaders are compiled during loading screens, or during gameplay in seamless world titles, such as Assassin's Creed IV, Batman: Arkham Origins, and the aforementioned Watch Dogs. During loads their compilation increases the time it takes to start playing, and during gameplay increases CPU usage, lowering frame rates. When the shader is no longer required, or the game is closed, it is discarded, forcing its recompilation the next time you play.
- ↑ NVIDIA - SLI Antialiasing - last accessed on 2016-10-12
- "SLI AA essentially disables normal AFR rendering, and in 2-way mode will use the primary GPU for rendering + forced AA, while the secondary GPU is only used to do AA work.
In SLI8x mode for example, each GPU would then do 4xMSAA after which the final result becomes 4xMSAA+4xMSAA=8xMSAA.
This can be useful in games without proper SLI support, so at least the second GPU is not just idling.
However it unfortunately only works correctly in OpenGL, and there will be no difference in temporal behavior between for example normal forced 4xMSAA+4xSGSSAA and SLI8x+8xSGSSAA in DX9."
- "SLI AA essentially disables normal AFR rendering, and in 2-way mode will use the primary GPU for rendering + forced AA, while the secondary GPU is only used to do AA work.
- ↑ https://www.manualslib.com/manual/557432/Nvidia-Quadro-Workstation.html?page=120